WebBench源码阅读.md
Webbench是一个在linux下使用的非常简单的网站压测工具。它使用fork()模拟多个客户端同时访问我们设定的URL,测试网站在压力下工作的性能,最多可以模拟3万个并发连接去测试网站的负载能力。 |
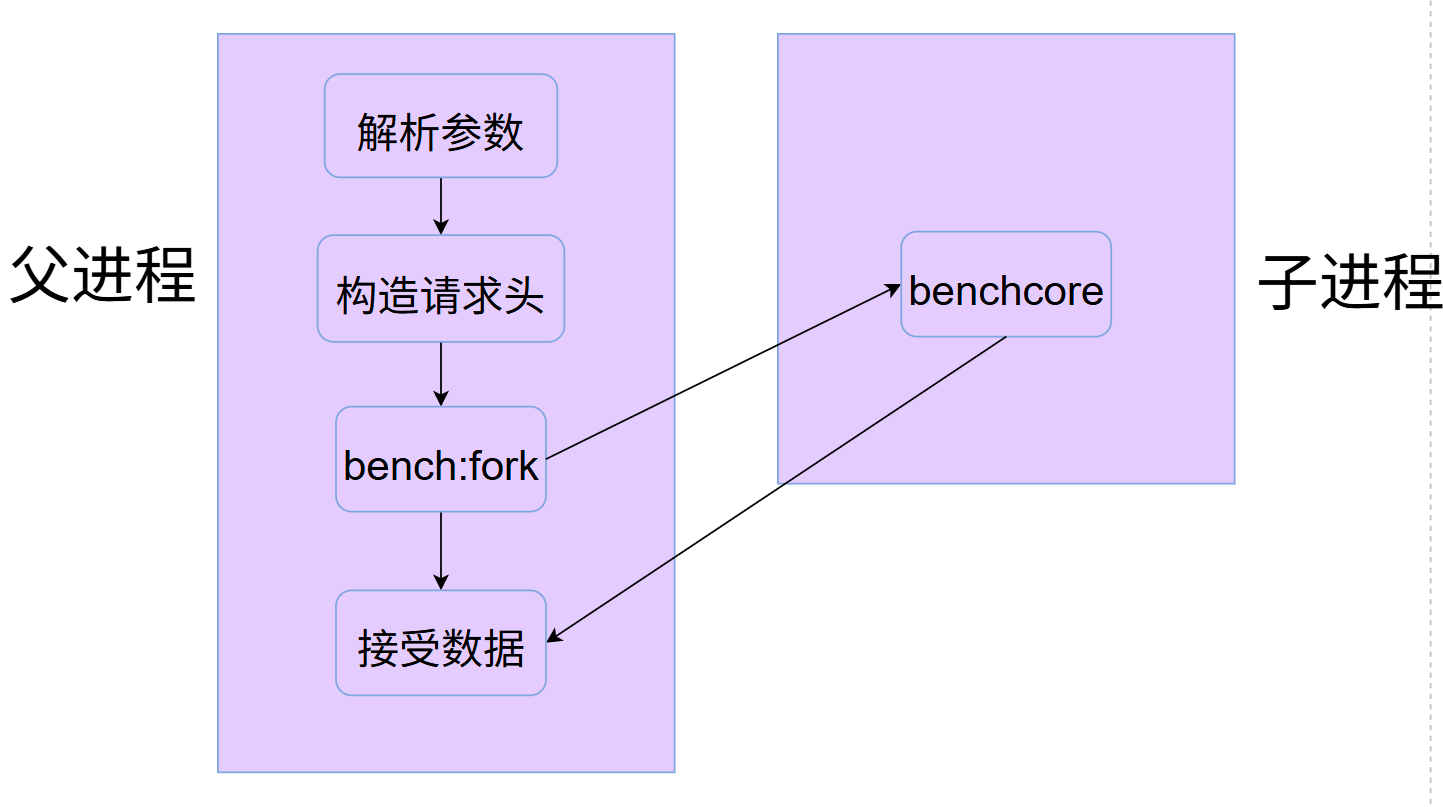
项目结构
代码细节
main
- 首先使用
getopt_long解析参数并初始化程序。
while((opt=getopt_long(argc,argv,"912Vfrt:p:c:?h",long_options,&options_index))!=EOF ) |
optarg:
这个是getopt和getopt_long函数族中的全局变量,用于存储命令行选项的参数值。如果某个选项有参数值(如-o output.txt),那optarg会设置为指向output.txt字符串的指针。
- 利用
optind找到命令行参数中网站的url,然后调用build_request向对应网站发送请求
if(optind==argc) { |
optind:
下一个待处理参数的索引,默认从1开始,跳过args[0]程序名。
关于这里的
fprintf为什么使用stderr输出:stdout通常用于程序的实际结果输出,这些内容可能是用户需要重定向到文件或管道的数据。stderr用于日志、错误、调试信息或非核心内容。即使stdout被重定向,stderr仍会直接显示在终端。
build_request
通过用户参数构造请求头。
void build_request(const char *url) |
strcspn(url + i, "/")的功能解析:
这个函数调用用于 从字符串url + i的位置开始,查找第一个出现/字符的位置,并返回从起始位置到该字符的 长度(字节数)。
最终效果大概如下:
GET /test.jpg HTTP/1.1 |
bench
- 该函数首先调用自己封装的接口
Socket创建目标主机间的套接字并使用connect连接,测试是否成功,如果没有成功就退出程序;否则关闭连接。 - 使用
pipe()创建pipe用于子进程和主进程之间通信。 - 创建子进程调用
benchcore进行测试,将测试结果写入pipe,主进程读取结果。
static int bench(void) |
fdopen():
FILE *fdopen(int fd, const char *mode);将 已有的文件描述符 包装成 标准文件流,从而允许使用fgets、fread等高级函数
benchcore
- 自定义超时信号处理函数,如果超时就设置
timerexpired = 1;用alarm()设置超时时间,如果超时就会发送SIGALRM信号 - 进行压力测试。如果没有超时,就一直访问这个网页。
void benchcore(const char *host,const int port,const char *req) |
相关函数
getopt_long
函数原型:
#include <getopt.h> // 必须包含此头文件 |
getopt_long是一个用于命令行解析的C语言库函数,它是对getopt的扩展,支持长选项和短选项。
该函数有以下解析功能:
短选项
单字符选项,通常以-开头,例如-h、-v。./program -h -v
长选项
多字符选项,以--开头,例如--help、--version。./program --help --version
带参数的选项
选项可以接受参数,例如--output=file.txt或-o file.txt。./program -o output.txt
./program --output=output.txt
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来自 Ya0rk の Blog!